What is a Carpenter Bee?
Nine distinct families, or groups, comprise the twenty thousand species of bees. These families are further categorized into three major groups based on the average length of the bee’s tongue, or proboscis.
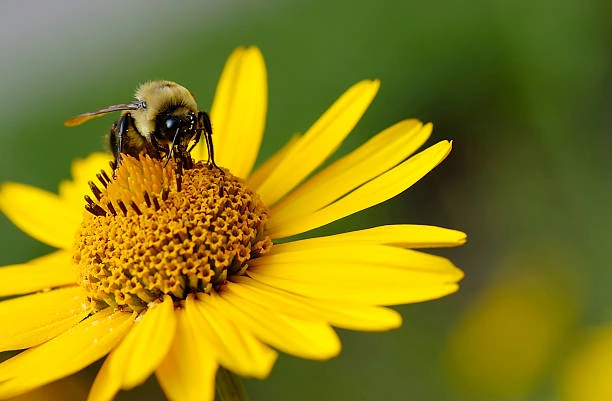
Carpenter bees are mostly solitary insects that belong to the family Apididae, which includes long-tongued bees. Along with the bumble bee, the carpenter bee is the largest native bee in the United States. The name of this bee comes from the way it burrows into hard materials, such as bamboo or wood, to make its nests.
Carpenter bees are excellent pollinators for many of the flowering plants in our gardens, on farms, and in natural areas–and according to Penn State Extension, 15% of our agricultural crops are pollinated by native bees like the carpenter bee. Here we can learn about different types and facts about carpenter bees.

Types of Carpenter Bees
There are hundreds of types of carpenter bee species found all over the world, and each varies in its appearance, location, and overall behavior. Following are some types of carpenter bees
Violet Carpenter Bee
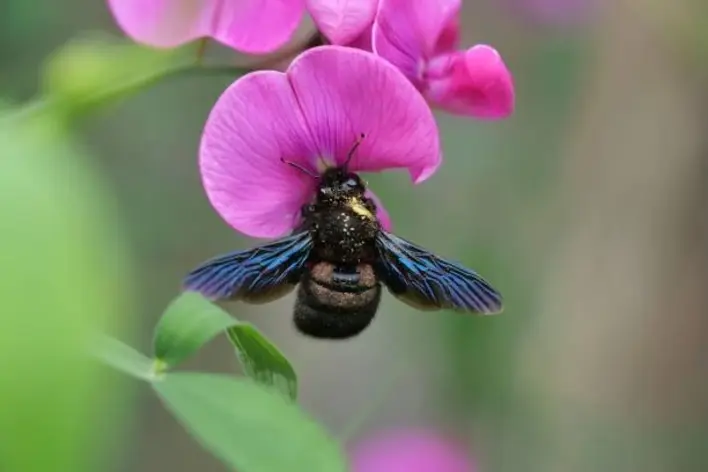

Violet Carpenter Bee is a black bee with dark wings, which in bright light shine purple or blue. This carpenter bee, native to Asia, is active from February to June, raising one and sometimes two broods each year. They start making nests in deadwood, grass stalks, or bamboo canes in April They also nest in wooden houses and are sometimes regarded as pests (although this bee is not aggressive to humans and rarely stings).
The most common types include the Eastern Carpenter Bee and the California Carpenter Bee.
Eastern Carpenter Bees
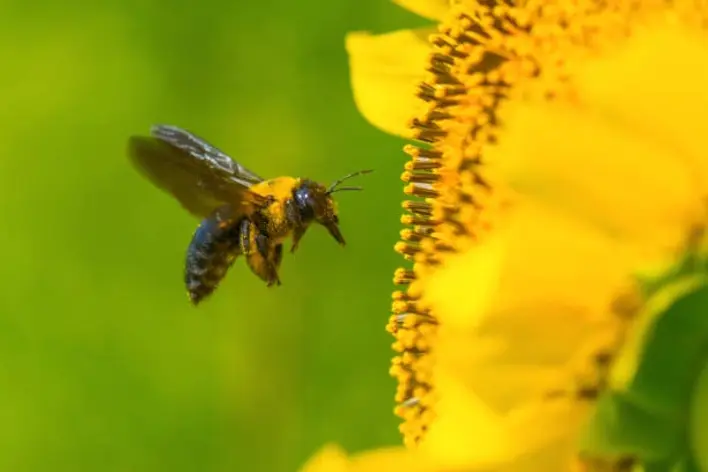

The Eastern variety, often seen in the eastern parts of North America, boasts a shiny black abdomen with a yellowish or white patch. According to BestBeeBrothers.com, the Eastern Carpenter bee prefers to build their nests out of structural timbers, such as cedar and pine.
California Carpenter Bees
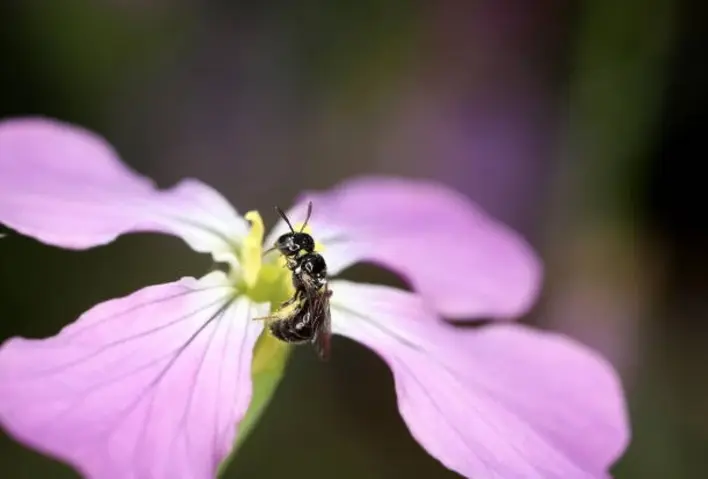

California Carpenter Bee, found in the western regions, showcases a striking metallic blue-black appearance.This carpenter bee makes its nest by creating long, double-ended passages in the limbs of oak trees.
These buzzing artisans, despite their differences, share common traits such as solitary living and wood-burrowing habits.
Carpenter Bee Quick Facts
Solitary Insects
Carpenter bees, in contrast to honeybees, are solitary insects, meaning they do not form colonies. Each female carpenter bee takes the initiative to create and maintain her own individual nest.
Woodworking Experts
These bees are skilled woodworkers. They create nests by burrowing into wood, typically choosing soft or decaying timber.
Distinct Appearance
Carpenter bees are often recognized by their robust bodies and shiny abdomen. Some species may have patches of yellow or white on their bodies.
Limited Bees Sting Risk
While female carpenter bees are capable of stinging, they are not aggressive and rarely pose a threat. Male carpenter bees, often more visible, do not have stingers.
Nesting Preferences
For nesting, carpenter bees favor wood that has not been painted or treated. Common nesting sites include eaves, decks, and wooden structures.
Pollination Role
Despite their reputation for wood-boring, carpenter bees play a significant role in pollination as they visit flowers to collect nectar.
Short Lifespan
Although the lifespan of an adult carpenter bee is relatively short, typically ranging from a few weeks to a few months, it is influenced by environmental conditions.
Seasonal Activity
Spring and summer are when carpenter bees are most active.They may become less active or dormant during colder seasons.
Diverse Species
There are different species of carpenter bees found in various regions. Common types include the Eastern Carpenter Bee and the California Carpenter Bee.
Wood Damage
While carpenter bees do not consume wood, their nesting habits can cause structural damage over time. Preventive measures such as painting or treating wood can help mitigate potential harm.
Male vs. Female carpenter bees
In the buzzing world of carpenter bees, knowing the difference between the male and female members adds an interesting layer to their story.
Female Carpenter Bees
Female carpenter bees are the architects, responsible for creating and maintaining nests by burrowing into wood. They wield stingers but are generally mild-mannered unless provoked.
Male Carpenter Bees
On the other hand, male carpenter bees, often more visible with their hovering antics, don’t have stingers. Instead of drilling into wood, they focus on their other critical role—mating. These guys are the pollinators, flitting from flower to flower, contributing to the cycle of life. While both genders play vital roles in the carpenter bee narrative
| Characteristics | Male Carpenter Bee | Female Carpenter Bee |
| Head Color | Possesses a white mark or spot on his head. | Completely black |
| Roles and Responsibility | Defends its territory and nests | digs holes and burrows wood to construct nests. |
| Stingers | Has no stingers | Has stingers on her back |
| Temperament | More aggressive | More even-tempered |
| Nectar Robbing | slightly more damaging to the structure of the flower than females. | Not as guilty of stealing nectar as males areExtremely destructive to flower structure |
FAQs
Q: Do carpenter bees make honey?
No, Carpenter bees do not make honey, despite the fact that they pollinate flowering plants and consume nectar. Read more
What is the relationship between carpenter bees and beeswax?
Carpenter bees are not known for producing beeswax. Beeswax is primarily produced by honey bees.
Do Carpenter Bees Sting?
Yes, female carpenter bees can sting, but they are generally not aggressive. They may sting if they feel threatened or cornered.
Are Carpenter Bees Harmful to Humans?
Carpenter bees are not harmful to humans in the same way that some stinging insects can be. However, their nesting habits can cause structural damage to wooden structures.
What Wood Do Carpenter Bees Prefer?
Carpenter bees prefer untreated or unpainted wood. They commonly nest in softwoods like cedar, redwood, or pine.
Do Carpenter Bees Live in Colonies?
No, carpenter bees are solitary insects. Each female creates her individual nest, and they do not live in colonies like honeybees.
Are Male Carpenter Bees Aggressive?
Male carpenter bees do not have stingers, so they are unable to sting. They are often more visible with their hovering behavior and play a crucial role in pollination.
How Long Do Carpenter Bees Live?
The lifespan of a carpenter bee varies, but adults typically live for several weeks to a few months, depending on environmental conditions.
Do Carpenter Bees Cause Damage to Homes?
While carpenter bees don’t consume wood, their nesting habits can cause structural damage over time. Preventive measures such as painting or treating wood can help mitigate potential harm.
Can I Prevent Carpenter Bee Infestations?
Yes, you can prevent carpenter bee infestations by painting or treating exposed wood surfaces, using wood varnish, or employing professional pest control measures.